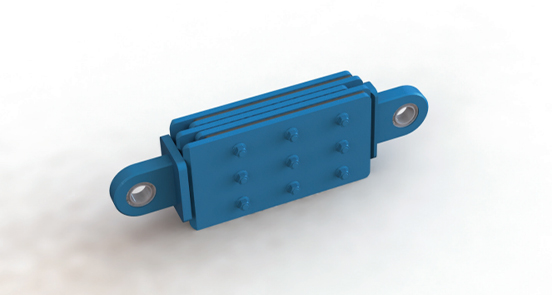
1. Composite friction damper
Composite friction damper is a type of seismic damping product for building structures, which utilizes the deformation of rubber and the sliding of friction plates to provide a certain degree of stiffness and damping for the structure. When an earthquake occurs, relative motion occurs between the two ends of the damper. The inner friction damper generates friction, consuming seismic energy, while the outer viscoelastic damper generates elastic and damping forces, consuming seismic force. At the same time, the viscoelastic damper provides stiffness for structural resetting.

Figure 1 Effect diagram of composite friction damper
2. Product composition and material technical indicators
2.1 Product composition
The composite friction damper consists of a large side plate, friction plate, friction plate, core plate, rubber, pin head, etc.

Figure 2 Composition diagram of composite friction damper
2.2 Product Material Technical Indicators
(1) The friction material of the damper should be made of polymer composite materials;
(2) The rubber of the damper should be used;
(3) Other materials can use ordinary steel that meets the requirements of the Steel Structure Design Specification.
3. Deepening design requirements
(1) The arrangement of composite friction dampers and connectors shall not affect the appearance and functional use of the building;
(2) When designing nodes, it is necessary to ensure that the nodes and connectors are in an elastic state under rare earthquakes;
(3) The product supplier shall submit node and connector design calculations and drawings for design approval;
(4) Product suppliers should deepen their nodes according to the typical node form provided in the design based on their own product structure, and should not arbitrarily change the node form.
4. Composite friction damper technology
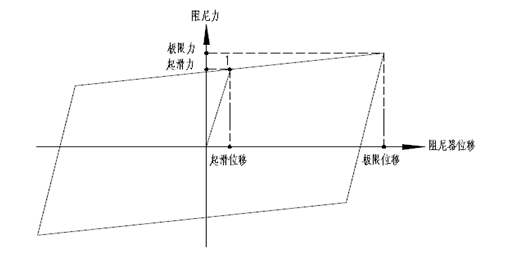
Figure 3 Mechanical performance diagram of composite friction damper
(2) The mechanical parameters of the damper should be determined by reciprocating static loading tests, and the hysteresis curve of the damper should be full without obvious pinching phenomenon. The product shall be cycled for 30 cycles under the designed displacement amplitude and 3 cycles under 1.2 times the displacement amplitude. The main mechanical parameters of the damper shall not decrease by more than 15%;
(3) All dampers do not enter a sliding state under wind loads that occur once every ten years.
(4) The performance curve of the composite friction damper is shown in the following figure:
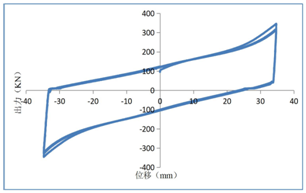
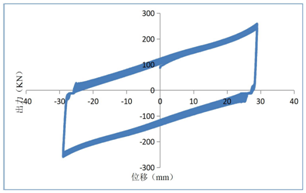
图四 力学性能曲线 图五 疲劳曲线
5. Composite friction damper testing:
5.1 Third party testing
Engineering dampers must have a certificate of qualification from a third-party testing organization with testing qualifications. The number of third-party inspection samples shall not be less than 3% of the same type and specification of the same project. When the number of damper products of the same type and specification is small, 3% of the total number of samples can be taken from the same type of damper, but not less than 2, with a 100% pass rate. At least 1 sample shall be taken for fatigue performance testing of 30 cycles of reciprocating under rare earthquake design displacement. After being inspected, it shall not be used for the main structure.
5.2 Factory inspection
The dampers used in this project must be 100% tested and have a certificate of conformity affixed before leaving the factory. The testing content includes:
(1) Effective dimensions of each part of the damper: not exceeding ± 2mm of the product design value;
(2) The surface of the damper should be flat, without mechanical damage, rust, or burrs.
5.3 Testing report of composite friction dampers


Figure 6 Inspection Report
6. Surface treatment requirements for composite friction dampers
6.1 Surface coating requirements for composite friction dampers
序号 | 涂装程序 | 油漆名称 | 涂装颜色 | 涂装道数 | 涂装方法 | 涂装场所 | 干膜厚度 (μm) |
1 | 表面处理 | 采用预处理流水线进行除锈处理,除尽铁锈、水分等杂物。 涂装由专业喷涂车间完成。表面处理质量达到 GB8923规定的 Sa2.5级,表面粗糙度 40-80μm后, | |||||
2 | 底漆 | 拜迪环氧富锌底漆BH232 | 锌灰 | 1 | 无气喷涂 | 工厂车间 | 40~50 |
3 | 封闭漆 | 拜迪丙烯酸脂肪聚氨酯面漆 | 中灰 | 1 | 无气喷涂 | 工厂车间 | 40~50 |
6.2 Surface coating requirements for composite friction damper node plates:
序号 | 涂装程序 | 油漆名称 | 涂装颜色 | 涂装道数 | 涂装方法 | 涂装场所 | 干膜厚度 (μm) |
1 | 表面 处理 | 采用预处理流水线进行除锈处理,除尽铁锈、水分等杂物。 涂装由专业喷涂车间完成。表面处理质量达到 GB8923规定的 Sa2.5级,表面粗糙度 40-80μm后, | |||||
2 | 底漆 | 拜迪环氧富锌底漆BH232 | 锌灰 | 1 | 无气喷涂 | 工厂车间 | 40~50 |
3 | 封闭漆 | 拜迪丙烯酸脂肪聚氨酯面漆 | 中灰 | 1 | 无气喷涂 | 工厂车间 | 40~50 |
7. Installation of dampers
7.1 Installation process
(1) According to the requirements of the design drawings, before installing the damper, mark the corresponding position on the structure and recheck the axis, elevation, etc;
(2) During the construction of the main structure, install embedded parts and connecting nodes, including node plates, high-strength bolts, chemical anchor bolts, etc., and pour them as a whole with the main structure;
(3) Install dampers after the completion of the main structure construction;
(4) Sealing and rust prevention treatment.
7.2 Weld requirements
(1) Welding materials must meet regulatory requirements;
(2) The on-site weld seam is a secondary weld seam;
(3) The welding of composite friction dampers should be carried out in accordance with the general welding process documents of the project;
(4) Any matters not covered shall be handled in accordance with the relevant regulations listed in the first item of this instruction.
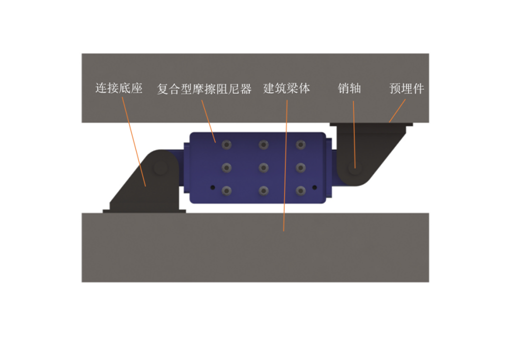
Figure 7 Installation rendering
8. Construction acceptance
8.1 Construction Inspection
阶段 | 检查项目 | 数量 | 检查方法 | 判定标准 | 处理 |
安装时 | 安装精度 | 全部 | 目视 | 安装误差在标准值以内 | 修正 |
外观 | 全部 | 目视 | 不应发生材料脱落、生锈 | 修正 | |
安装完毕 | 螺栓状况 | 全部 | 目视 | 螺栓、螺母应连接可靠 | 替换 |
8.2竣工检查
阶段 | 检查项目 | 数量 | 检查方法 | 判定标准 | 处理 |
竣工检查 | 本身 | 全部 | 目视、接触 | 不出现异常、损伤 | 修正 |
生锈 | 全部 | 目视 | 不应有生锈 | 修正 | |
安装完毕 | 全部 | 目视 | 螺栓、螺母应连接可靠 | 替换 |