
Metal yielding is one of the effective ways to consume seismic input energy, which can control the dynamic response of structures by utilizing the good hysteresis performance of metal materials entering the elastic-plastic range. The metal yield type energy dissipator was initially proposed by Kelly et al., including forms such as torsion beam, bending beam, and U-shaped steel, thus pioneering the concept of energy dissipation and vibration reduction in the field of seismic engineering.
Soft steel damper is a type of metal, elastic-plastic, displacement related damper.
Soft steel damper is a structural seismic device made of special soft steel, which is prone to yield and consumes high energy. It mainly utilizes the non elastic characteristics of special soft steel plates after yielding to consume energy input from external excitations such as earthquakes in the structure. It belongs to displacement related energy dissipation and vibration reduction devices. The use of soft steel plates has the advantages of low yield point, durability, and long-term use without maintenance. Its seismic performance is not affected by temperature, and it is currently a cost-effective product among various energy dissipation and shock absorption devices.
Metal dampers consume the energy generated by earthquakes through the elastic-plastic deformation of metals. It has been widely used in seismic design of structures. When designing dampers, setting the resistance force of the damper to be lower than the yield force of the structure and improving the damper's own plastic deformation ability are two key factors. Earthquake energy can usually be consumed through the plastic deformation of soft steel through reciprocating bending, tension, compression, and shear energy.
2. Common materials for soft steel
Mild steel is a low yield stress steel, with a yield point generally between 80-150 MPa and an elongation at fracture of 40-60%. Mild steel has good low cycle fatigue and hysteresis properties. The materials commonly used in the production of soft steel are shown in Table 1:
Table 1 Composition Chemistry of Soft Steel Materials
材质符号 | 厚度 | 化学成分% | |||||
C | Si | Mn | P | S | N | ||
BLY100 | 6≦t≦50 | ≦0.1 | ≦0.03 | ≦0.2 | ≦0.025 | ≦0.015 | ≦0.006 |
BLY160 | ≦0.05 | ≦0.1 | ≦0.4 | ≦0.025 | ≦0.015 | ≦0.006 | |
BLY225 | ≦0.1 | ≦0.05 | ≦0.5 | ≦0.025 | ≦0.015 | ≦0.006 | |
Table 2 Physical properties of commonly used core plate materials for soft steel dampers
材质符号 | 屈服点(N/mm2) | 抗拉强度(N/mm2) | 伸长率(%) |
BLY100 | 100+20 | 200-300 | ≥50 |
BLY160 | 160+20 | 220-320 | ≥45 |
BLY225 | 225+20 | 300-400 | ≥40 |
3. Performance parameters of soft steel dampers
As one of the scientific research achievements in energy dissipation and seismic reduction systems in the field of structural engineering, soft steel dampers have been widely used in the construction field in recent years. Many engineering application examples have shown that soft steel dampers not only greatly improve the disaster resistance ability of structures, but also save a considerable proportion of construction costs compared to traditional structural design methods. Its application areas include:
(1) RC/SRC steel structure construction project;
(2) Structural seismic reinforcement and reinforcement engineering;
(3) Civil buildings, commercial public buildings, industrial factory buildings, lifeline engineering.
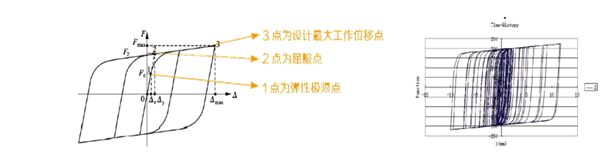
① For the elastic limit point: F § elastic limit load; Δ § Elastic ultimate displacement;
② The yield point of the damper corresponds to the yield force Fy and yield displacement Δ y;
③ The point is the maximum working displacement point of the damper design, corresponding to the maximum yield force Fmax and the maximum yield displacement Δ max
Installed soft steel damper 1 Structural deformation, resulting in displacement 1
Installed soft steel damper 2 Structural deformation, resulting in displacement 2
4. Features of soft steel dampers
(1) Clear shock absorption mechanism and significant shock absorption effect;
(2) Stable hysteresis characteristics;
(3) Good low cycle fatigue characteristics;
(4) Not affected by ambient temperature;
(5) Soft steel dampers have a simple appearance, simple structure, symmetrical and compact structure, convenient installation, small installation space, and easy replacement after earthquakes;
(6) Excellent fire resistance and durability;
(7) The energy dissipation of component materials is direct, without the use of other auxiliary materials;
5. Installation of soft steel dampers
(1) Installation of embedded parts
Review the installation position and dimensions of the working face (if the embedded parts have been installed in place, review the installation space of the damper), install the upper and lower connecting plates, and leave space that meets the installation requirements of the damper. Clean the work surface and prepare for subsequent construction.
Requirement: The embedded parts should be in the same plane as the centerline of the installation frame, perpendicular to the column and parallel to the beam, without any obvious angle.
(2) Damper positioning
Lift the damper into position using a gourd or lifting equipment, ensuring that the damper is horizontal and vertical, and then weld and fix the embedded connection plate.
(3) Complete installation
After reviewing the damper position to meet the drawing requirements, perform full welding operations according to the welding seam requirements and welding sequence (bolt anchoring requires special use)
Welding requirements: If there are no requirements, the quality inspection of the weld seam shall be level two. The weld seam shall be flat and uniform, with consistent texture, and there shall be no undercutting, slag inclusion, or virtual (omitted) welding.
(4) Inspection and acceptance
The installed damper needs to be inspected and accepted by the supervisor or professional inspection, and the hidden inspection record should be kept before entering the next process.
(5) Painting treatment
Perform fire and rust prevention treatment on dampers (welds) and apply the specified topcoat according to the drawing requirements.
