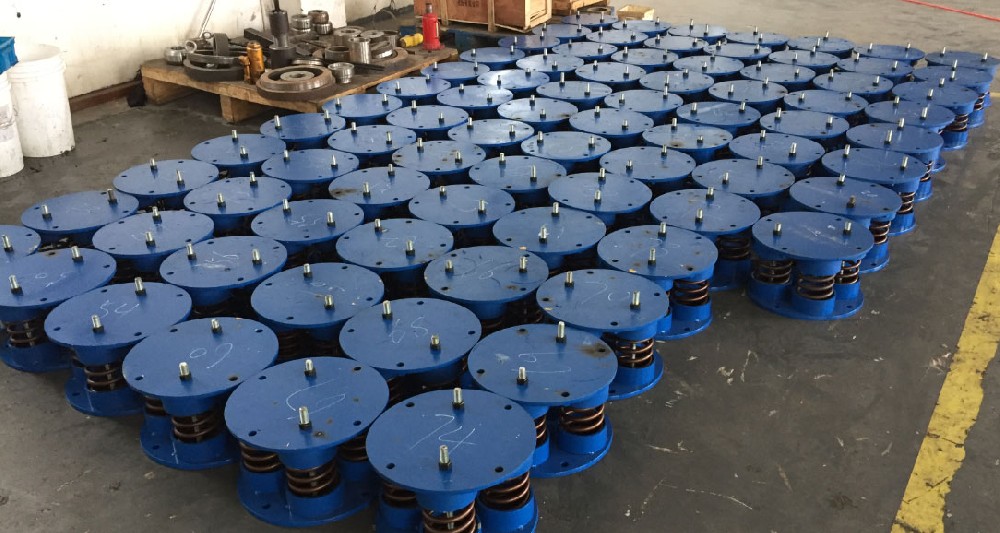

1. Industry demand analysis
With the urbanization process in our country, environmental vibrations caused by urban transportation have become an important factor affecting large laboratories, optical instruments and equipment, and the comfort of residents' lives. Subway, light rail, and motor vehicles transmit the vibrations they generate to the surrounding environment through tracks and roads.
Vibration and noise are the main aspects of urban rail transit that affect the environment. With the development of urban rail transit in recent years, people have paid more and more attention to this issue. Reducing the vibration and noise of rail transit is one of the keys to improving the quality of life of residents along the line and promoting the sustainable development of rail transit. When the train passes through, if the track surface and wheel tread are absolutely smooth, the wheel rail will not produce vibration directly, and the noise will be in an extremely weak state. There are various types of irregularities in the track surface and wheel tread, and the track structure and vehicle body will vibrate when trains pass through.
When a train passes through a track at a certain speed, both the vehicle and the track will vibrate in various directions in space. The reasons for the strength of the vibration are: the static and dynamic irregularity of the track geometry; Wave shaped wear on the top surface of the steel rail and rail joints; The speed of the train, wheel tread scratches, uneven wheel tread, and so on. Due to the coupling relationship between the vibration of the vehicle and track systems, this coupling vibration ultimately needs to be transmitted through the track structure to form an output. For elevated structures, they are transmitted to the ground through bridge piers and abutments. For the subway, it is transmitted to the surface through the soil medium around the tunnel. As a vibration source, the track structure is also an important link in the vibration propagation path, directly affecting the final vibration effect. Studying the vibration reduction performance of rail transit from the perspective of vibration sources and transmission factors is the optimal solution.
The operation route of urban rail transit inevitably passes through areas that are particularly sensitive to vibration, such as factories, hospitals, laboratories, etc., where precision instruments are installed. When the vibration reaches a certain intensity, it will affect the normal use of precision instruments in these areas.
When a car is driving on an uneven road surface, the wheels will generate additional dynamic loads on the road surface. This dynamic load will accelerate the attenuation of road surface smoothness, and the deterioration of road surface smoothness will increase the additional dynamic loads generated by the wheels on the road surface. Therefore, the unevenness of road surfaces is considered one of the main factors affecting vehicle vibration response. It is usually assumed that road surface roughness is a stationary, zero mean Gaussian stochastic process, and power spectrum is used to describe the statistical characteristics of the road surface. A large number of tests and studies have been conducted on road surface spectra both domestically and internationally, such as the national standard GB7031-86 "Method for representing road surface roughness under vehicle vibration input" and the 150 SCIPWG4 developed by the International Association for Standardization.

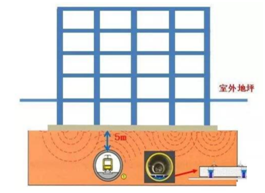
With the continuous enhancement of China's economic strength and the increasing investment in scientific research, the use of optical equipment, precision instruments, metal and other instruments such as lithography machines, scanning electron microscopes, MEMS, energy spectrometers, etc. is becoming more and more widespread. These precision instruments have extremely high requirements for the operating environment, and their environmental vibration amplitude is required to be in the range of um and 0.1 um. Once these instruments and equipment are placed in laboratories close to urban transportation, the anti micro vibration design of precision instruments and equipment needs to be urgently addressed.


Photolithography machine JEM-f200 field emission transmission electron microscope


MEMS oscillator energy spectrometer
2、 Typical plan
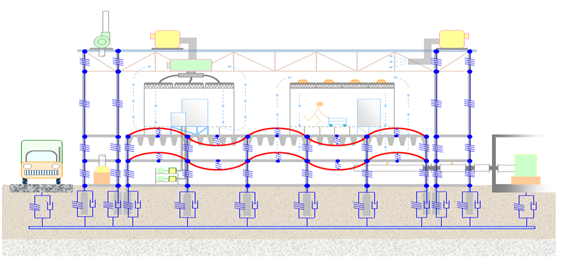
Firstly, preliminary testing is required, followed by system design. We can start by setting up isolation ditches, increasing foundation quality, and implementing low-frequency micro vibration control systems. Finally, we can conduct project acceptance testing.
1. Preliminary testing:


2. System design:
Main measures: 1) Set up vibration isolation ditches;
2) Increase basic quality;
3) Low frequency micro vibration control system;
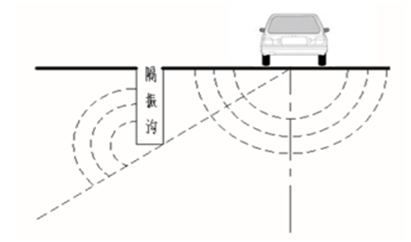
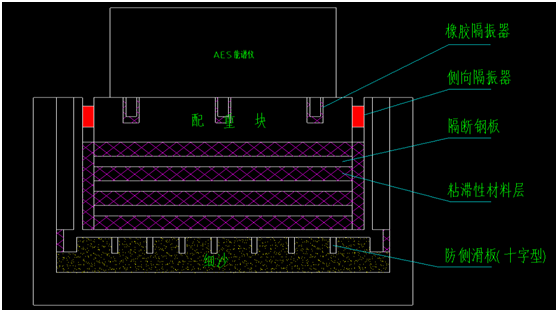
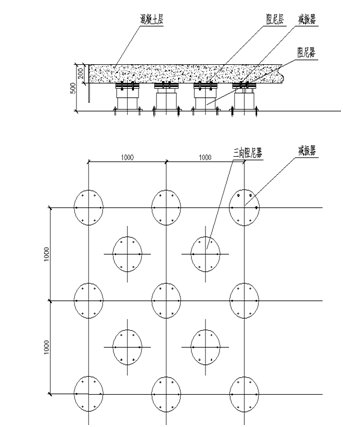
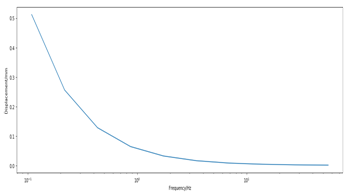
 地面载荷谱
地面载荷谱
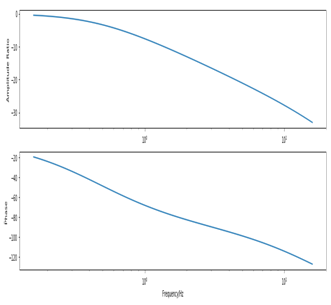
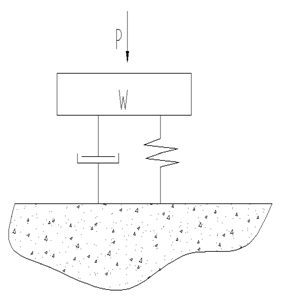
振动传递关系
3、典型案例-中电54所微波实验室




三.产品选型
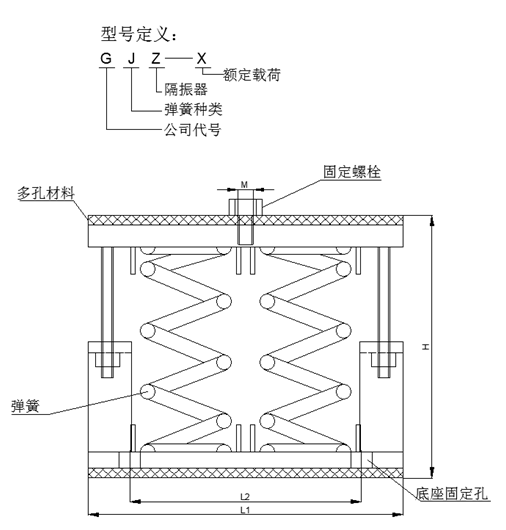
型号 | 荷载(N) | 变形量(mm) | 竖向刚度(N/MM) | 自振频率(Hz) | 外形尺寸(mm) | |||||
预压 | 额定 | 最大 | H | L1 | L2 | M | ||||
GTJ-50 | 300 | 500 | 600 | 5 | 4 | 1.5 | 160 | 340 | 300 | 14 |
GTJ-100 | 600 | 1000 | 1200 | 5 | 9 | 1.5 | 160 | 340 | 300 | 14 |
GTJ-200 | 1500 | 2000 | 2400 | 5 | 18 | 1.5 | 160 | 340 | 300 | 16 |
GTJ-300 | 2800 | 3000 | 3600 | 5 | 27 | 1.5 | 160 | 400 | 350 | 16 |
GTJ-400 | 3700 | 4000 | 4800 | 5 | 35 | 1.5 | 160 | 400 | 350 | 20 |
GTJ-500 | 4800 | 5000 | 6000 | 5 | 44 | 1.5 | 160 | 400 | 350 | 20 |
GTJ-600 | 5500 | 6000 | 7200 | 5 | 53 | 1.5 | 160 | 450 | 380 | 20 |
以上参数为标准型,可以根据客户要求进行定制设计。